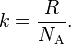| Values of k | Units | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1.38064852(79)×10−23 | J/K | SI units, 2010 CODATA value, J/K = m2⋅kg/(s2⋅K) in SI base units[1] |
| 8.6173324(78)×10−5 | eV/K | 2010 CODATA value[1] 1 electronvolt = 1.602176565(35)×10−19 J[1]
1/k = 11604.519(11) K/eV
|
| 2.0836618(19)×1010 | Hz/K | 2010 CODATA value[1] 1 Hz⋅h = 6.62606957(29)×10−34 J[1] |
| 3.1668114(29)×10−6 | EH/K | EH = 2R∞hc = 4.35974434(19)×10−18 J[1] = 6.579683920729(33) Hz⋅h[1] |
| 1.0 | Atomic units | by definition |
| 1.38064852(79)×10−16 | erg/K | CGS system, 1 erg = 1×10−7 J |
| 3.2976230(30)×10−24 | cal/K | 1 steam table calorie = 4.1868 J |
| 1.8320128(17)×10−24 | cal/°R | 1 degree Rankine = 5/9 K |
| 5.6573016(51)×10−24 | ft lb/°R | 1 foot-pound force = 1.3558179483314004 J |
| 0.69503476(63) | cm−1/K | 2010 CODATA value[1] 1 cm−1 ⋅hc = 1.986445683(87)×10−23 J |
| 0.0019872041(18) | kcal/(mol⋅K) | per mole form often used in statistical mechanics—using thermochemical calorie = 4.184 joule |
| 0.0083144621(75) | kJ/(mol⋅K) | per mole form often used in statistical mechanics |
| 4.10 | pN⋅nm | kT in piconewton nanometer at 24 °C, used in biophysics |
| −228.5991678(40) | dBW/(K⋅Hz) | in decibel watts, used in telecommunications (see Johnson–Nyquist noise) |
| 1.442 695 041... | Sh | in shannons (logarithm base 2), used in information entropy (exact value 1/ln(2)) |
| 1 | nat | in nats (logarithm base e), used in information entropy (see Planck units, below) |
The Boltzmann constant (kB or k), named after Ludwig Boltzmann, is a physical constant relating energy at the individual particle level with temperature. It is the gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA:
The Boltzmann constant has the dimension energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. The accepted value in SI units is1.38064852(79)×10−23 J/K.
Since k is a physical constant of proportionality between temperature and energy, its numerical value depends on the choice of units for energy and temperature. The small numerical value of the Boltzmann constant in SI units means a change in temperature by 1 K only changes a particle's energy by a small amount. A change of 1 °C is defined to be the same as a change of 1 K. The characteristic energy kT is a term encountered in many physical relationships.